Advanced Manufacturing Industry in Lithuania
- Why Lithuania
- Future vision
- Key investment areas
- Already here
- Downloads
- News & Events
- Why Lithuania
- Future vision
- Key investment areas
- Already here
- Downloads
- News & Events
Lithuania is your gateway to Industry 4.0 success. The country stands at the forefront of the manufacturing and business services sectors, powered by a rich tradition in engineering and a focus on innovation. The manufacturing sector is a cornerstone of the Lithuanian economy, driven by a highly skilled workforce and a robust technology sector that accelerates digital transformation. The government’s commitment to innovation, efficiency, and green transformation further bolsters the country’s status as a premier destination for advanced manufacturing and global business services.
Key Advantages
of Manufacturing
in Lithuania

Talent Availability
Lithuania boasts a diverse talent pool fluent in 35 languages, excelling in both traditional engineering disciplines and cutting-edge IT fields. With 13% of the workforce employed in manufacturing, Lithuania offers ample opportunities for new businesses to scale rapidly and retain top talent. The country is home to the largest technical university in the Baltic states, Kaunas Technology University (KTU), which nurtures a pipeline of highly educated IT and engineering professionals.
-
5th in the EUfor science, math, computing, engineering, manufacturing and construction bachelor graduates in the young adult populationSource: Eurostat, 2022
-
58%of the population aged 25-34 has a higher education (4th in the EU)Source: Eurostat, 2021
-
13%of Global Business Services centers in Lithuania deliver engineering (non-IT) solutions, while 22% of centers perform R&D functionSource: Lithuania's Business Services report, 2023
-
1st in the EU56% of scientists and engineers are womenSource: Eurostat, 2023
-
1st globallyfor digital skills availabilitySource: IMD World Competitiveness Yearbook, IMD World Competitiveness Center, 2023
-
3rd in the EUfor equality in labor force participation: 50% of the total labor force is female in LithuaniaSource: IMD World Talent Ranking, 2023
Continuous Focus on Talent Development
Infrastructure and Connectivity
Lithuania provides top-tier infrastructure, from high-quality roads and logistics hubs to reliable digital networks. Its strategic location offers seamless access to the EU market, supported by , a major seaport, and an extensive rail network, including the upcoming Rail Baltica project. The country’s e-infrastructure ranks among the best globally, ensuring robust and secure digital connectivity.
-
Connected by sea, air, road and rail
-
Lithuania’s 3 international airports provide access to major European cities within 2-3 hours.
-
Klaipėda State Seaport is the leading port in the Eastern Baltics for container handling.
-
Rail connections to Western Europe and Asia. The Rail Baltica railway will connect Lithuania to Finland to Germany for both passenger and freight traffic by 2030.
-
Well-developed logistics infrastructure, with the logistics sector contributing 12% to Lithuania’s GDP.
-
-
Robust, resilient, and secure e-infrastructure
-
-
2nd in CEE
for digital quality of lifeSource: Surfshark Digital Quality of Life Index, 2023
-
2nd in the EU
for fixed broadband priceSource: Digital Economy and Society Index, 2023
-
6th globally
for cybersecuritySource: ITU Global Cybersecurity Index, 2021
-

Government Support and Financial Incentives
Lithuania offers substantial government support and financial incentives for manufacturing businesses. Companies can benefit from grants for research and development, tax exemptions in Free Economic Zones (FEZ), and streamlined regulatory processes. These incentives ensure quick establishment and smooth operation.
Unlock the benefits of Lithuania’s Green Corridor for advanced manufacturing investments
The Green Corridor initiative fast-tracks large-scale investment projects with 0% corporate tax for 20 years, streamlined planning, and faster decision-making from public authorities, ensuring smoother setup and long-term success.
Future-focused Manufacturing in Lithuania
Innovation Ecosystem
Lithuania’s innovation landscape is driven by government initiatives, academic research, and industry collaboration. Innovation hubs and a growing startup ecosystem support the development of advanced manufacturing technologies, while the regulatory framework provides incentives for R&D development.
-
Multiple innovation valleys provide services to manufacturing innovators
-
-
5%corporate profit tax for patented products
-
3xdeductible expenses for R&D
-
Sustainable Manufacturing
Lithuania is committed to energy sustainability, aiming for 100% renewable energy in the final balance of electricity consumption by 2028 and becoming a green hydrogen producer by 2026. The country’s manufacturing sector integrates environmentally friendly practices, reducing energy consumption and adopting circular economy principles.
-
-
70%
In 2024, 70% of the country’s total energy output was produced from renewable sources.Source: Ministry of Energy, 2025
-
696M EUR
earmarked for renewable energy expansion under the LT100 support scheme.Source: Ministry of Finance, 2023
-
2.8 GW
of offshore wind power to be generated in Lithuania by 2040Source: Ministry of Energy, 2024
-
-
Expected share of renewable energy in the final balance of electricity consumption in Lithuania
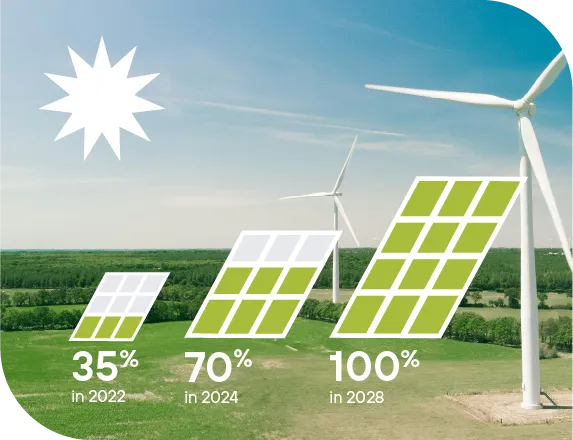 Source: Ministry of Energy, 2025
Source: Ministry of Energy, 2025
Your Best Choice for Manufacturing
Advanced Manufacturers in Lithuania
Lithuania’s appeal is reflected in the success of global companies like Kinze, Festo, and Yara, which have leveraged the country’s business-friendly environment, skilled workforce, and efficient logistics to thrive.
Want to learn more about advanced manufacturing opportunities?
Lithuania has a lot to offer, and we’re here to help you discover it. At Invest Lithuania, our team is here to make your business journey smoother. From connecting you with the right people to accessing valuable resources, we take care of the details so you can drive your business forward.
Related materials
to download
What’s happening
in the sector
-
 ManufacturingMarine Technology to invest €15M in advanced manufacturing expansion in KlaipėdaFeb 03, 2026
ManufacturingMarine Technology to invest €15M in advanced manufacturing expansion in KlaipėdaFeb 03, 2026 -
 ManufacturingLithuania Defence Services to invest nearly €50 million in military equipment manufacturingDec 12, 2025
ManufacturingLithuania Defence Services to invest nearly €50 million in military equipment manufacturingDec 12, 2025 -
 New investmentsGroundbreaking ceremony in Baisogala: Rheinmetall and Lithuania build artillery ammunition plant on NATO’s eastern flankNov 04, 2025
New investmentsGroundbreaking ceremony in Baisogala: Rheinmetall and Lithuania build artillery ammunition plant on NATO’s eastern flankNov 04, 2025